Planck’s Radiation Law
- This is application of Bose-Einstein statistics.
- According to quantum theory, the radiant energy occurs in energy packets.
- These packets are known as quanta or photon.
- The energy of packet should be h times the frequency of photon.
- The momentum of each packet should be h/c times the frequency of photon.
- The photons are indistinguishable particles having zero rest mass and having spin quantum number 1.
- Thus photons are Bose particle and hence Bose Einstein statistics can be applied on it.
- By using Planck’s radiation law, we can also establish the Rayleigh Jean’s law, Wein’s law and Stefan-Boltzmann’s law.
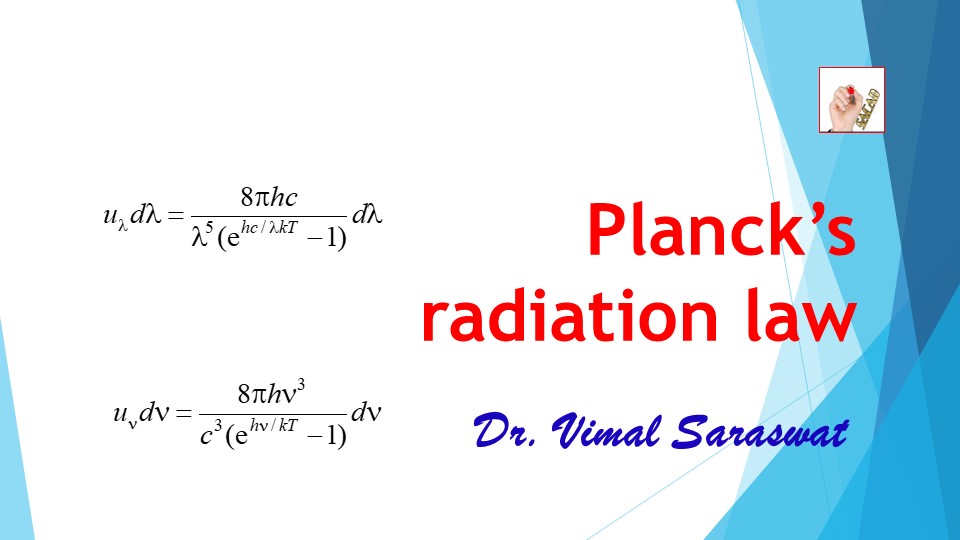
Planck’s radiation law
- According to Planck, the energy density of radiations emitted from a black body in the wavelength range λ and λ + dλ is, uλ dλ = (Nλ dλ) E
- Here Nλ dλ = Number of oscillators (number of modes of vibration) in the wavelength range λ and λ + dλ
- E is average energy of Planck’s oscillator.
This is Planck’s radiation formula in terms of wavelength.
This is Planck’s radiation formula in terms of frequency
To know more about Planck’s radiation formula click here.


Short and useful